Innovative processes for the production of polymer-based particles
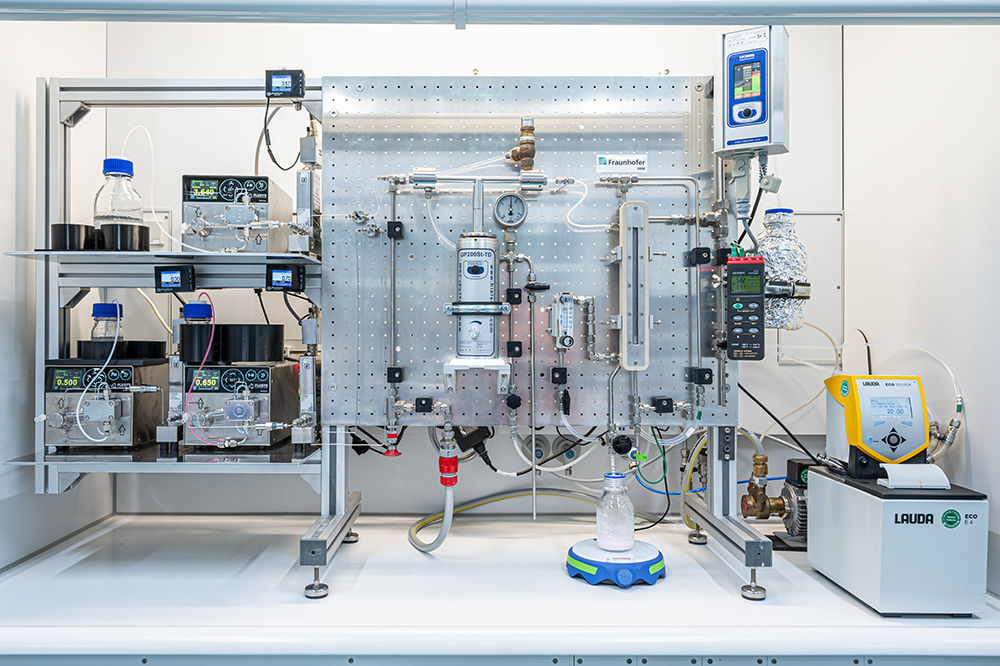

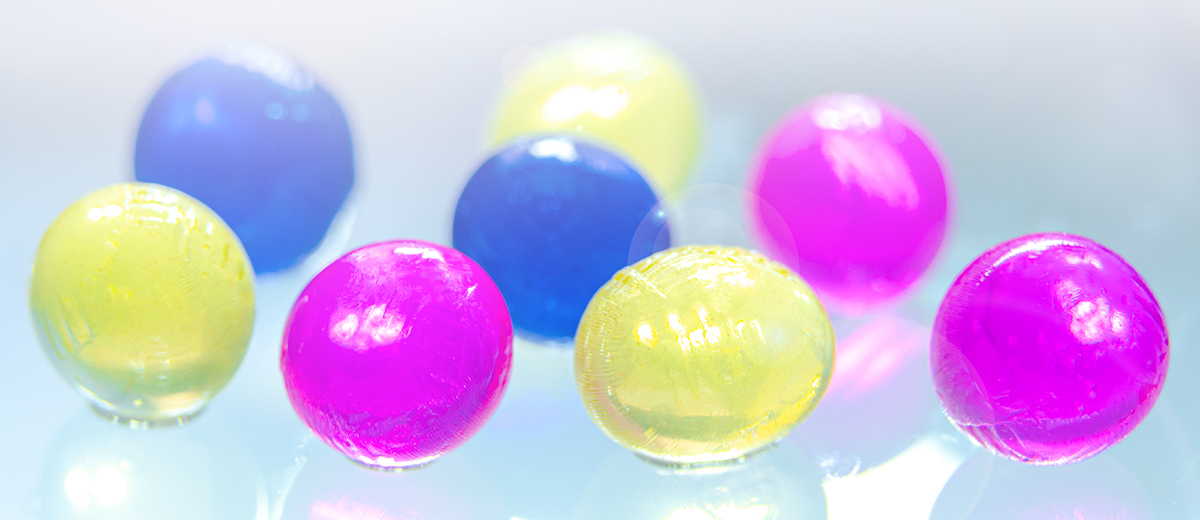
The targeted encapsulation of active ingredients is a key building block for numerous applications – from pharmaceuticals to food technology and material development. The protective capsule wall effectively shields sensitive ingredients from external influences such as light, oxygen or moisture. At the same time, the capsule structure enables controlled release, increases stability and extends the shelf life of the ingredients. Additionally, it allows the simultaneous introduction of incompatible substances into a single formulation – a crucial advantage for modern product developments.
At Fraunhofer IMM, we focus on the development and optimization of polymer-based particles and capsules. These play a key role in the creation of innovative materials with customized properties. Both micro- (larger than 1 µm) and nanoscale (smaller than 1 µm) particles open up a wide range of technological possibilities.
Depending on the application requirements, we realize homogeneous particle structures as well as complex morphologies – including capsules with a “core-shell” structure or variants with several active cores. Our precise manufacturing processes enable the targeted adaptation of functionality, size and structure – delivering high-performance solutions for demanding markets.
Customized particles for maximum product performance
"Our technology is the bodyguard that gets your ingredient safely to its destination."
The targeted encapsulation of active ingredients is a key building block for numerous applications – from pharmaceuticals to food technology and material development. The protective capsule wall effectively shields sensitive ingredients from external influences such as light, oxygen or moisture. At the same time, the capsule structure enables controlled release, increases stability and extends the shelf life of the ingredients. Additionally, it allows the simultaneous introduction of incompatible substances into a single formulation – a crucial advantage for modern product developments.
At Fraunhofer IMM, we focus on the development and optimization of polymer-based particles and capsules. These play a key role in the creation of innovative materials with customized properties. Both micro- (larger than 1 µm) and nanoscale (smaller than 1 µm) particles open up a wide range of technological possibilities.
Depending on the application requirements, we realize homogeneous particle structures as well as complex morphologies – including capsules with a “core-shell” structure or variants with several active cores. Our precise manufacturing processes enable the targeted adaptation of functionality, size and structure – delivering high-performance solutions for demanding markets.
 Fraunhofer Institute for Microengineering and Microsystems IMM
Fraunhofer Institute for Microengineering and Microsystems IMM
